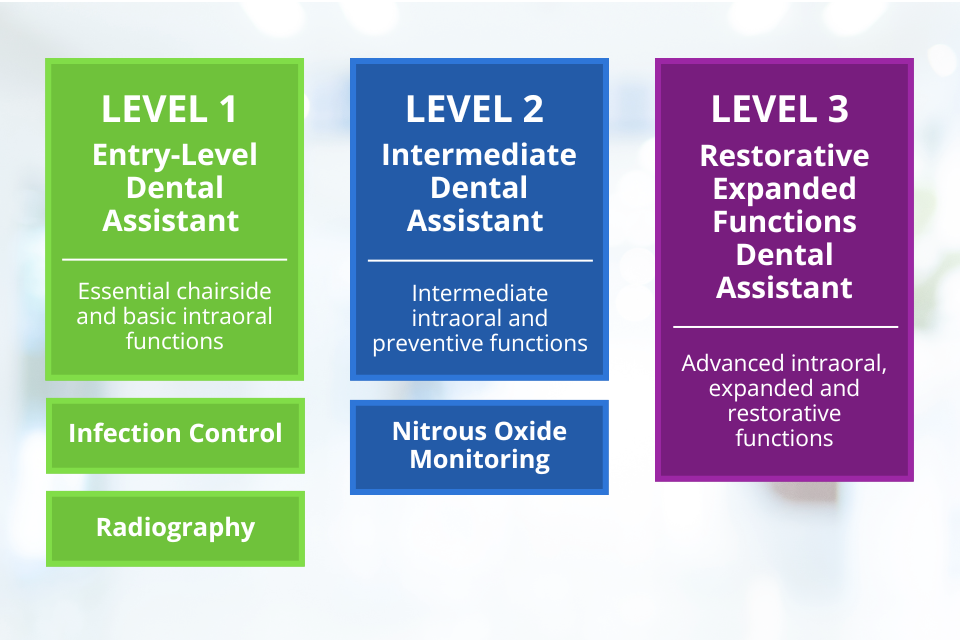
Dental Assisting Professional Model
Addressing the needs of the profession
Dentistry is experiencing challenges related to the workforce, including an insufficient number of qualified dental assistants. A shared understanding of what dental assistants do and how they can advance will greatly improve dentistry’s ability to recruit and retain qualified personnel, and to develop pipelines for the future workforce. That’s why representatives from across dentistry created the Dental Assisting Professional Model.
 | |||
| Overview and toolkit | Download the model |
Endorsements
The Dental Assisting Professional Model has earned endorsements from leading dental organizations that recognize its potential to strengthen the profession and build a consistent, qualified workforce. Their endorsement underscores the growing support for more professional uniformity — and invites others across dentistry to join in advancing this shared vision.
- American Association of Dental Boards
- American Dental Assistants Association
- American Dental Education Association
- American Network of Oral Health Coalitions
- Association for Dental Safety
- Aspen Dental
- D&D Dental Consulting
- Dental Assisting National Board
- Imagine Orthodontic Studio
- Pennsylvania Coalition for Oral Health
- Wyoming Professional Training
Media coverage
Dental Assisting Professional Model Workgroup to hold first meeting
Dentistry wants universal rules for dental assisting in the U.S.
Survey shows agreement in the profession for dental assisting advancement
Dental Assisting Professional Model Workgroup moves draft framework forward
Universal framework for dental assistants moves one step closer
Contact Us
Want to learn more about the model, how it can be used, or how you can endorse it? Fill out the form and we'll get back in touch.Workgroup members
The Dental Assisting Professional Model was developed by a workgroup of 20 members, including dental assistants, dentists, educators, dental hygienists, and regulators. Members were nominated by several dental organizations, including the American Association of Dental Administrators, American Association of Dental Boards, American Dental Assistants Association, American Dental Association, American Dental Education Association, American Dental Hygienists’ Association, Association of Dental Support Organizations, Dental Assisting National Board, Hispanic Dental Association, and National Network for Oral Health Access.


